Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that simplifies the method of recording transactions and tracking assets in a network. It's a constantly growing list of records known as a block. These blocks are connected, creating a chain known as a blockchain.
The fundamental feature of blockchain :
Immutable and Unhackable records
Distributed ledger technology
Persistent in storing data (no loss of data)
Setting up Virtualenv & Installing Dependencies 🔌
create a virtualenv, using python's built-in module called venv. Here env is the name of the environment.
python3 -m venv env
for activating this virtualenv, we need to source it.
source ./env/bin/activate
Installing Dependencies
we need flask as a dependency for serving our blockchain
pip install Flask==2.2.2
Setting up Folder Structure 🗂
create a base folder, and name it blockchain
inside this folder create a file called blockchain.py which will hold our blockchain code.
create another file called server.py this will contain our server code, to server our blockchain.
Creating ⚒️ a Blockchain
Import Dependencies
import datetime
import json
import hashlib
import time
Now, create a class called blockchain, which will hold all our logic and chain itself. Inside this blockchain class, we will have some functions.
init: initialize the blockchain, and creates a Genius Block
Genius Block is the name given to the first block that is created or mined when any block is initialized.
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""
initialize the blockchain
"""
self.chain = []
# create the genesis block
self.create_block(proof=1, previous_hash="0")
- create_block: this function creates a new block and adds it to the blockchain, it takes proof and the previous hash as an argument
def create_block(self, proof, previous_hash):
"""
add a new block to the blockchain
"""
block = {}
block["index"] = len(self.chain) + 1
block["timestamp"] = str(datetime.datetime.now())
block["proof"] = proof
block["previous_hash"] = previous_hash
self.chain.append(block)
return block
- get_previous_block: This function gets the previous block, which is added to the blockchain
def get_previous_block(self):
"""
get the previous block
"""
return self.chain[-1]
proof_of_work: proof of work is a Consensus Protocol in blockchain used to define finding a number such that the hash of the number, is hard to find because it takes a lot of time, and computing power.
in this case, we are using the sha256 hash function, and we are looking for a number such that the hash of the number starts with 4 zeros. if the hash of the new proof and the previous proof starts with 4 zeros, then the proof is valid and we can add it to the blockchain.
def proof_of_work(self, previous_proof):
start_time = time.time()
new_proof = 1
check_proof = False
while check_proof is False:
hash_operation = hashlib.sha256(
str(new_proof**2 - previous_proof**2).encode()
).hexdigest()
if hash_operation[:4] == "0000":
check_proof = True
else:
new_proof += 1
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(' time take to get new_proof using pow : ', elapsed)
return new_proof
- hash: hash function takes a block and converts it into hash using sha256, and returns the hash
def hash(self, block) -> str:
"""
hash the block using sha256, and return the hash
"""
encoded_block = str(json.dumps(block, sort_keys=True)).encode('utf-8')
hash = hashlib.sha256(encoded_block).hexdigest()
return hash
- is_chain_valid: check if the blockchain is valid
def is_chain_valid(self, chain):
"""
check if the blockchain is valid
"""
if chain == [] or chain == None:
# if the chain is empty or None, then the chain is not passed as a parameter
chain = self.chain
previous_block = chain[0]
block_index = 1
while block_index < len(chain):
block = chain[block_index]
if block["previous_hash"] != self.hash(previous_block):
return False
previous_proof = previous_block["proof"]
proof = block["proof"]
hash_operation = hashlib.sha256(
str(proof**2 - previous_proof**2).encode()
).hexdigest()
if hash_operation[:4] != "0000":
return False
previous_block = block
block_index += 1
return True
Creating ⚒️ a web server
Creating a Flask web server
import os
from flask import Flask, jsonify
# env
PORT = os.getenv('PORT', 8080)
DEBUG = os.getenv('DEBUG', True)
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/', methods=['GET'])
def home():
return "<h1>Welcome to the Blockchain</h1>", 200
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=PORT, debug=DEBUG)

Importing our blockchain
importing and initializing blockchain will create Genius Block
from blockchain import Blockchain
blockchain = Blockchain()
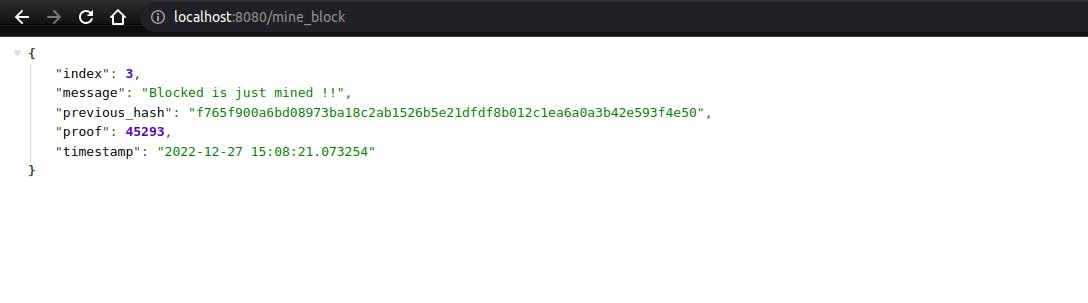
Adding mine_block function
This mine_block function helps used to mine a block in a given blockchain
@app.route('/mine_block', methods=['GET'])
def mine_block():
previous_block = blockchain.get_previous_block()
previous_proof = previous_block['proof']
proof = blockchain.proof_of_work(previous_proof)
previous_hash = blockchain.hash(previous_block)
block = blockchain.create_block(proof, previous_hash)
response = {}
response['message'] = "Blocked is just mined !!"
response['index'] = block['index']
response['timestamp'] = block['timestamp']
response['previous_hash'] = block['previous_hash']
response['proof'] = block['proof']
return jsonify(response), 201
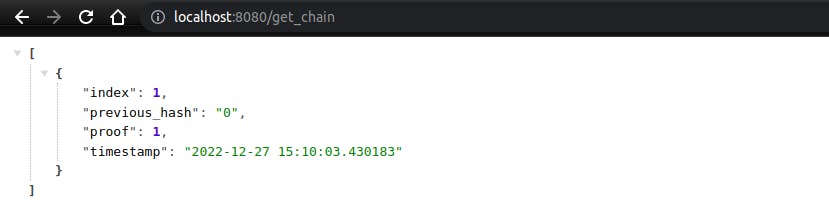
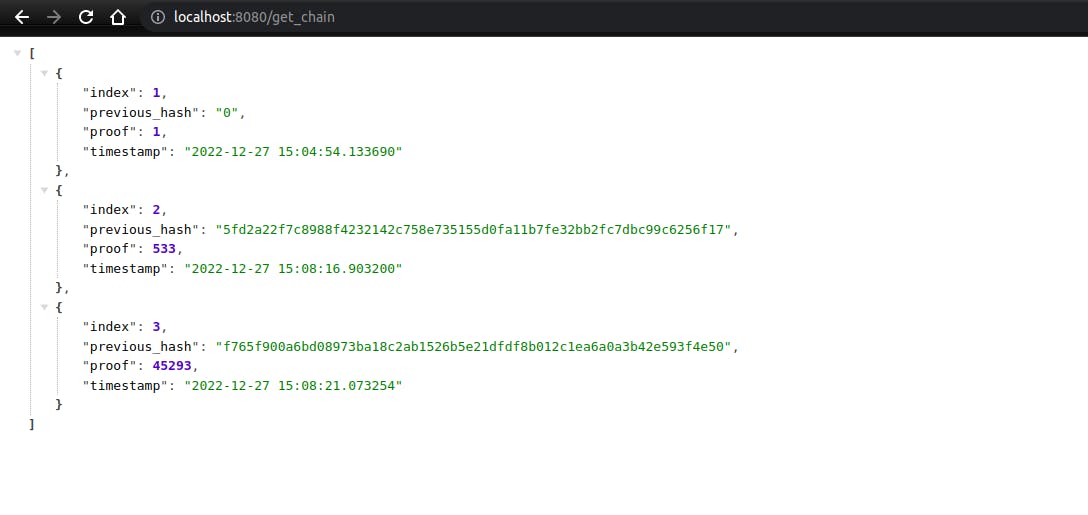
Adding get_chain function
This get_chain function will return a JSON list of blocks and its attribute.
@app.route('/get_chain', methods=['GET'])
def get_chain():
blockchain_clone = blockchain.get_chain()
return jsonify(blockchain_clone), 200
Adding is_valid function
This function checks if the current blockchain Is valid or not
@app.route('/is_valid', methods=['GET'])
def is_valid():
is_valid = blockchain.is_chain_valid(blockchain.chain)
if is_valid:
response = {}
response['message'] = "Blockchain is valid"
return jsonify(response), 200
else:
response = {}
response['message'] = "Blockchain is not valid"
return jsonify(response), 200

Starting ⚙️ webserver
To start the web server, we will execute the server.py
python3 server.py